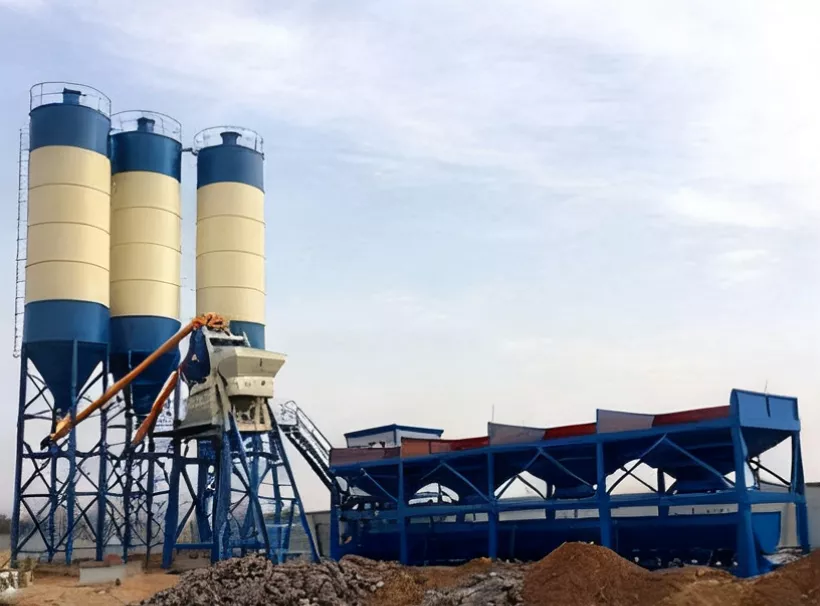
What is a concrete batching plant?
A concrete batching plant is a combined facility for centralized concrete mixing. It automatically weighs, transports, and mixes raw materials such as cement, aggregates (sand, gravel), water, and additives according to a preset mix ratio, ultimately producing fresh concrete.
These batching plants are essential for large construction projects, ensuring a stable and high-quality supply of concrete. There are various types of batching plants, including stationary and mobile, as well as different mixing methods such as wet mixing (all raw materials are mixed at the plant) and dry mixing (materials are mixed with water during transport to the construction site).

Haomei concrete batching plant for sale
We offer a full range of concrete batching plants with different capacities, suitable for small to large construction projects.
-
 HZS25 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS25 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 25 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 0.5 m³
-
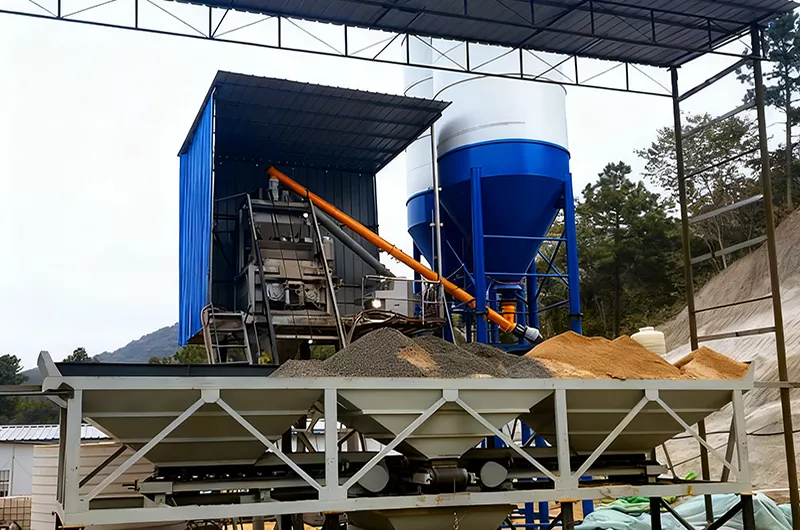 HZS35 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS35 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 35 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 0.75 m³
-
 HZS50 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS50 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 50 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 1.0 m³
-
 HZS60 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS60 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 60 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 1.0 m³
-
 HZS75 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS75 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 75 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 1.5 m³
-
 HZS90 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS90 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 90 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 1.5 m³
-
 HZS120 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS120 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 120 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 2.0 m³
-
 HZS150 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS150 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 150 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 3.0 m³
-
 HZS180 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS180 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 180 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 3.0 m³
-
 HZS240 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS240 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 240 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 4.0 m³
-
 HZS180-Q3000 Concrete Batching Plant
HZS180-Q3000 Concrete Batching Plant
Productivity: 200-270 m³/h | Mixer Capacity: 4.0 m³
All models are equipped with high-quality JS series mixers and PLD series batching machines, ensuring high efficiency and durability.
Concrete Batching Plant Technical Parameters
| Model | HZS25 | HZS35 | HZS50 | HZS60 | HZS75 | HZS90 | HZS120 | HZS150 | HZS180 | |
| Specification | Unit | Value | Value | Value | Value | Value | Value | Value | Value | Value |
| Productivity | m3/h | 25 | 35 | 50 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 |
| Capacity of Mixer | m3 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Mixer Power | kw | 18.5 | 18.5 | 37 | 37 | 44 | 44 | 74 | 110 | 110 |
| Discharge Height (for customers choice) | m | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Aggregate Bin | Quantity | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Aggregate Bin Capacity | m3 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 4.8 | 4.8 |
| Max. Weighing Value of aggregate | kg | 500 | 850 | 1000 | 1000 | 1300 | 1300 | 1500 | 1800 | 1800 |
| Max. Weighing Value of cement | kg | 300 | 500 | 800 | 800 | 1100 | 1100 | 1100 | 800 | 800 |
| Max. Weighing Value of water | kg | 160 | 300 | 350 | 350 | 500 | 500 | 1500 | 800 | 800 |
| Max. Weighing Value of additive | kg | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 40 | 40 | 60 | 50 | 50 |
| Aggregate Measuring Accuracy | % | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ±2% | ±2% | ±2% | ±2% |
| Water Measuring Accuracy | % | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ±1% | ±1% | ±1% | ±1% |
| Cement Measuring Accuracy | % | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ±1% | ±1% | ±1% | ±1% |
| Additive Measuring Accuracy | % | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ±1% | ±1% | ±1% | ±1% |
| Cement Silo | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | |
| Cement Screw Conveyor | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | |
| Cement Silo Capicity | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | Optional | |
| Control Mode | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control | Auto/Semi control |
Types of concrete batching plants
Types of Concrete Batching Plants by Mobility
| Type | Capacity Range | Features | Typical Applications |
| Mobile Concrete Batching Plant | 25–120 m³/h | Integrated structure, towable and movable, quick installation | Highways, bridges, temporary construction sites |
| Stationary Concrete Batching Plant | 60–240+ m³/h | High stability, strong automation, suitable for continuous production | Ready-mix concrete plants, large infrastructure projects |
| On-Site Concrete Batching Plant | 15–90 m³/h | Installed directly at the construction site, concrete is mixed and used immediately | Hydropower stations, tunnels, wind power projects |
Mobile Concrete Batching Plants
Mobile concrete batching plants are designed for easy transportation and quick installation at different job sites. All main components—such as the mixer, weighing system, conveyor, and control unit—are mounted on a single chassis or semi-trailer unit. This allows fast relocation without the need for complex foundation work.
Typical capacity: 25–120 m³/h
Applications:
Perfect for road construction, bridge projects, temporary construction sites, and remote areas where mobility and speed are crucial.
Stationary Concrete Batching Plants
Stationary concrete batching plants are designed for long-term and high-volume concrete production. Installed on a solid foundation, they feature high production capacity, stability, and automation. These plants are equipped with robust structures and advanced control systems to ensure consistent concrete quality.
Typical capacity: 60–240 m³/h (and above)
Applications:
Widely used in large infrastructure projects, commercial ready-mix concrete plants, and industrial-scale construction sites.
On-Site Concrete Batching Plants
On-site concrete batching plants are installed directly at the construction site to supply fresh concrete immediately as needed. They eliminate the need for concrete transportation from external plants, ensuring higher efficiency and consistent quality, especially for remote or large-scale projects.
Typical capacity: 15–90 m³/h
Applications:
Suitable for dams, tunnels, bridges, wind farms, and large-scale infrastructure projects in remote locations.
Types of Concrete Batching Plants by Capacity
| Type | Capacity Range | Features | Typical Applications |
| Small / Mini Concrete Batching Plant | 10–35 m³/h | Low cost, easy to move | Rural construction, small-scale projects |
| Compact Concrete Batching Plant | 20–60 m³/h | Modular, space-saving, easy to relocate | Urban construction, bridge projects |
| Standard / Large Concrete Batching Plant | 60–180+ m³/h | High automation, continuous production | Large infrastructure projects, ready-mix concrete plants |
Small / Mini Concrete Batching Plant
Mini concrete batching plants are small-capacity systems designed for small-scale construction or remote area projects. They are easy to install, require minimal foundation, and can be either stationary or portable.
Typical capacity: 10–35 m³/h
Applications:
Ideal for small residential construction, rural projects, and temporary construction sites. Haomei provides mini mobile concrete batching plants, small portable concrete batch plants, and small RMC plants.
Compact Concrete Batching Plants
Compact concrete batching plants are designed for quick installation and easy relocation. They feature a modular structure with pre-installed components, allowing for fast setup and efficient transport. These plants combine the advantages of stationary and mobile batching plants—offering high productivity while saving space.
Typical capacity: 20–60 m³/h
Applications:
Ideal for projects with limited space, frequent relocation, or where quick installation is required (e.g., urban construction sites, bridge projects).
Standard / Large Concrete Batching Plant
Standard or large concrete batching plants are high-capacity systems designed for continuous and large-scale concrete production. They feature strong structural design, advanced automation systems, and precise weighing equipment to ensure consistent concrete quality.
Typical capacity: 60–180 m³/h (and above)
Applications:
Widely used in major infrastructure projects, highways, bridges, airports, and commercial ready-mix concrete production.
Types of Concrete Batching Plants by Mixing Method
| Type | Mixing Location | Features | Typical Applications |
| Dry Mix Concrete Batching Plant | Mixed by the truck mixer | Low cost, quick relocation, suitable for long-distance transport | Ready-mix concrete suppliers |
| Wet Mix Concrete Batch Plant | Centralized mixing at the plant | High-quality concrete, good uniformity | High-quality projects, large infrastructure |
| Central Mix Concrete Batch Plant | Mixed in the plant’s main mixer | Excellent mixing effect, high production efficiency | Ready-mix plants, bulk supply |
| Ready Mix Concrete Batching Plants | Can be dry or wet | High automation, flexible supply | Urban construction, commercial projects |
Dry Mix Concrete Batching Plant
Dry mix concrete batching plants, also known as transit mix plants, measure and mix all dry ingredients (cement, sand, aggregates) before loading them into the mixer truck. Water is added only during transit in the truck mixer, allowing for flexibility in the concrete’s consistency at the construction site.
Typical capacity: 40–120 m³/h
Features:
- No central mixer required
- Simple structure and low initial cost
- Faster loading and batching process
- Suitable for long-distance transport
Applications:
Ideal for ready-mix concrete suppliers who deliver to multiple construction sites over wide areas.
Wet Mix Concrete Batching Plant
Wet mix concrete batching plants mix all materials—including water—at the central plant before discharging the fully mixed concrete into mixer trucks. This ensures high-quality and consistent concrete with uniform properties.
Typical capacity: 60–240 m³/h
Features:
- Equipped with a central mixer
- Ensures uniform mixing and consistent quality
- Ideal for high-performance concrete production
- Slightly higher initial investment
Applications:
Commonly used in large infrastructure, high-quality concrete projects, and commercial ready-mix plants.
Central Mix Concrete Batching Plant
Central mix plants are a subtype of wet mix batching plants. They produce fully mixed concrete in a central mixer, then transfer it into trucks for delivery. The main advantage is better control of the mixing process and improved concrete homogeneity.
Typical capacity: 90–300 m³/h
Features:
- Centralized mixing system
- High consistency and uniformity
- Reduced wear on truck mixers
- Efficient for large-scale RMC production
Applications:
Used in commercial RMC (Ready-Mix Concrete) plants and high-volume concrete supply operations.
Ready-Mix Concrete Batching Plant
Ready-mix concrete batching plants are designed for commercial concrete production. They can be configured as dry or wet types, depending on project needs. The produced concrete is delivered to clients via mixer trucks.
Typical capacity: 60–180 m³/h
Features:
- High automation and production efficiency
- Can produce different concrete grades and types
- Designed for continuous operation
- Centralized quality control system
Applications:
Used by commercial concrete suppliers and large-scale infrastructure construction companies.
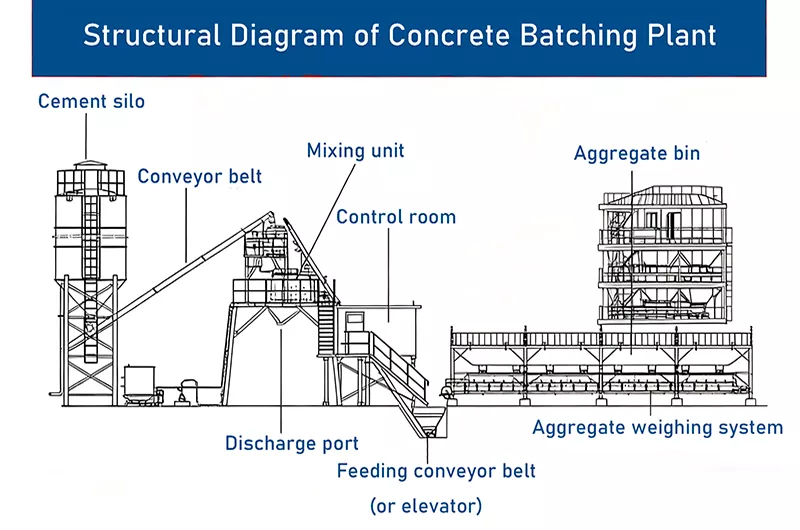
Core Components of a Concrete Batching Plant
A standard concrete batching plant typically includes the following key systems:
- Aggregate batching system: includes aggregate bins, belt conveyors, and weighing hoppers. Responsible for storing and proportionally weighing different sizes of sand and gravel.
- Powder storage and conveying system: includes cement silos, fly ash silos, and screw conveyors. Used to store and transport powdered materials like cement.
- Water and admixture system: includes water tanks, water pumps, admixture tanks, and metering devices. Responsible for accurately adding water and various liquid admixtures (such as water reducers and retarders).
- Control system: the "brain" of the entire batching plant, usually a computer control system that enables automated production, mix ratio input, data recording, and fault diagnosis.
- Mixing main unit: the core equipment that uniformly mixes all raw materials. Common types include twin-shaft forced mixers (high efficiency, excellent mixing quality) and planetary mixers.
- Concrete storage and delivery system: usually consists of the discharge hopper under the mixer, where concrete is directly unloaded into waiting concrete mixer trucks.
Concrete Batching Plant Specifications and Configurations
| Model | Theoretical Capacity (m³/h) | Configuration |
| HZS25 | 25 | JS500 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer, PLD800 concrete batching machine |
| HZS35 | 35 | JS750 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer, PLD1200 concrete batching machine |
| HZS50 | 50 | JS1000 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer, PLD1600 concrete batching machine |
| HZS60 | 60 | JS1000 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer, PLD1600 concrete batching machine |
| HZS75 | 75 | JS1500 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer |
| HZS90 | 90 | JS1500 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer, PLD2400 concrete batching machine |
| HZS120 | 120 | JS2000 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer |
| HZS150 | 150 | Mixers: JS3000 / JS2000 / JS2500 |
| HZS180 | 180 | JS3000 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer |
| HZS240 | 240 | JS4000 twin-shaft forced concrete mixer |
| HZS270 | 270 | Mixer: JS4500 |
Advantages / Importance of a Concrete Batching Plant
Consistency and Quality Control
Automated weighing and mixing ensure that each batch of concrete meets design requirements, reducing variability.
Efficiency
Rapid production of large quantities of concrete, which is crucial for large construction projects.
Cost Savings
On-site or nearby batching reduces concrete transportation costs.
Flexibility
Mobile batching plants can be set up flexibly as needed, especially suitable for remote or short-term projects.
Environmental / Regulatory Considerations
Batching plants are typically equipped with dust removal systems. Regulations (such as those from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, EPA) dictate plant operations to limit pollution.
Applications of a Concrete Batching Plant
Concrete batching plants are widely used in:
- Construction projects: buildings, bridges, roads, tunnels, dams
- Precast concrete production: manufacturing beams, blocks, slabs, and other concrete components
- Infrastructure projects: large-scale projects requiring massive amounts of concrete
- On-site or remote operations: with mobile concrete batching plants, mixing can be done near the point of use
How much does a concrete batch plant make?
| Model | Theoretical Capacity (m³/h) |
| HZS25 | 25 |
| HZS35 | 35 |
| HZS50 | 50 |
| HZS60 | 60 |
| HZS75 | 75 |
| HZS90 | 90 |
| HZS120 | 120 |
| HZS150 | 150 |
| HZS180 | 180 |
| HZS240 | 240 |
| HZS270 | 270 |
Related Equipment for Concrete Batching Plants
- twin shaft mixer batching plant
- fully automatic concrete batching plant
- oncrete batching plant cement silo
- silo batching plant
- mobile concrete silo
- portable concrete silo
- batching plant cement silo
- precast concrete batch plant
- hot mix batching plant
- tremie tube concrete
- volumetric batching plant
What are the problems with concrete batching plants?
- Unstable concrete quality: inaccurate batching or insufficient mixing can lead to inconsistent concrete batch quality.
- Equipment wear and failure: mixers, conveyors, and other equipment in a concrete batching plant are prone to faults due to aggregate abrasion.
- Dust and noise pollution: dust generated from cement and aggregates, as well as noise from mixing equipment, can affect the construction environment and nearby communities.
- Safety risks: operating concrete mixers and related equipment carries risks of mechanical injury and dust inhalation.
- Raw material supply issues: shortages of cement, aggregates, or additives may disrupt concrete production.
- Weather impact: extreme temperatures, rainfall, or wind can affect the production efficiency of the batching plant and concrete quality.


























































